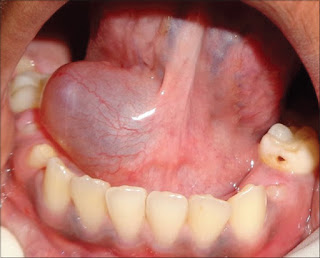
Hemangioma- A step by step approach
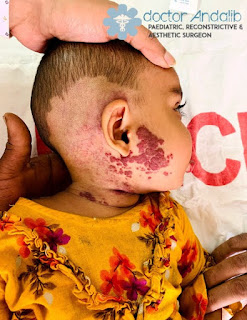
What is a hemangioma? Hemangioma is a vascular neoplasm or a vascular anomaly due to proliferation of blood vessels. They occur anywhere in the body, but skin and oral mucosa in the region of the lips, tongue, and buccal mucosa are most commonly affected. Therefore, the dentist or oral surgeon should be informed about their clinical aspect, diagnosis, and therapy. The gold standard for hemangioma treatment, especially for smaller circumscribed lesions and peripheral hemangiomas, is conventional surgical excision. However, complications that arise from conventional invasive surgical procedures such as excessive postoperative bleeding compelled the use of other different therapeutic alternatives including systemic corticosteroids, laser therapy, cauterization, cryotherapy, radiotherapy, and sclerotherapy. Hemangiomas are more common in girls than in boys. They are more common in premature infants, twins and Caucasian children. Most hemangiomas go through several phases of grow...